450 Million years ago
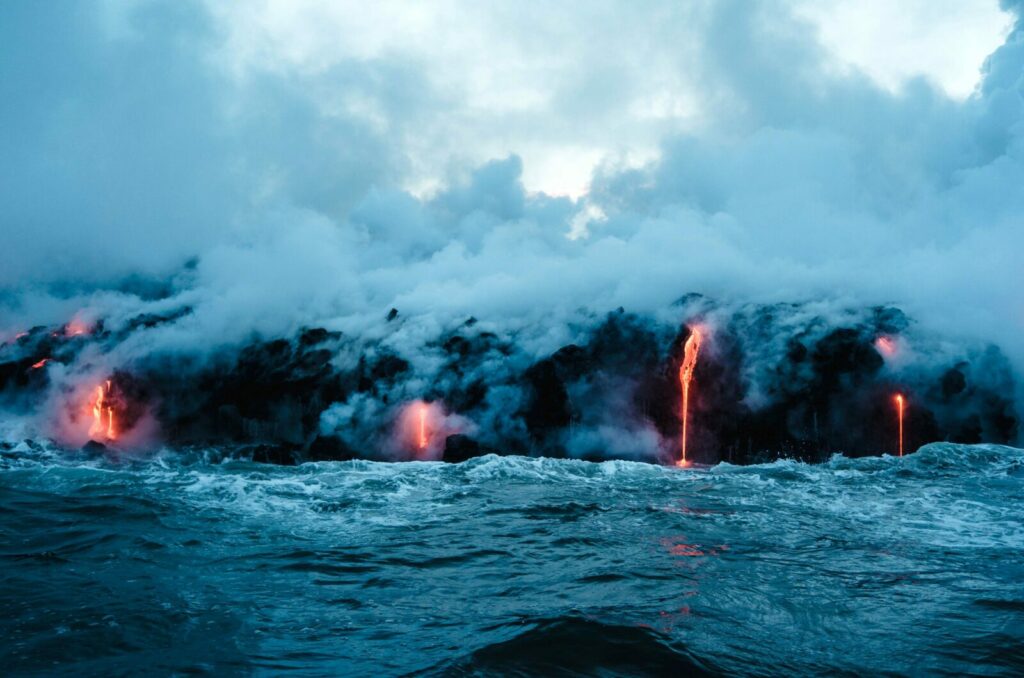

Rocks of Cwm Idwal are formed
Volcanic eruptions produce lava, ash and dust. Sediments gather on the bottom of a shallow ocean and compact over time to form rocks.
400 Million years ago
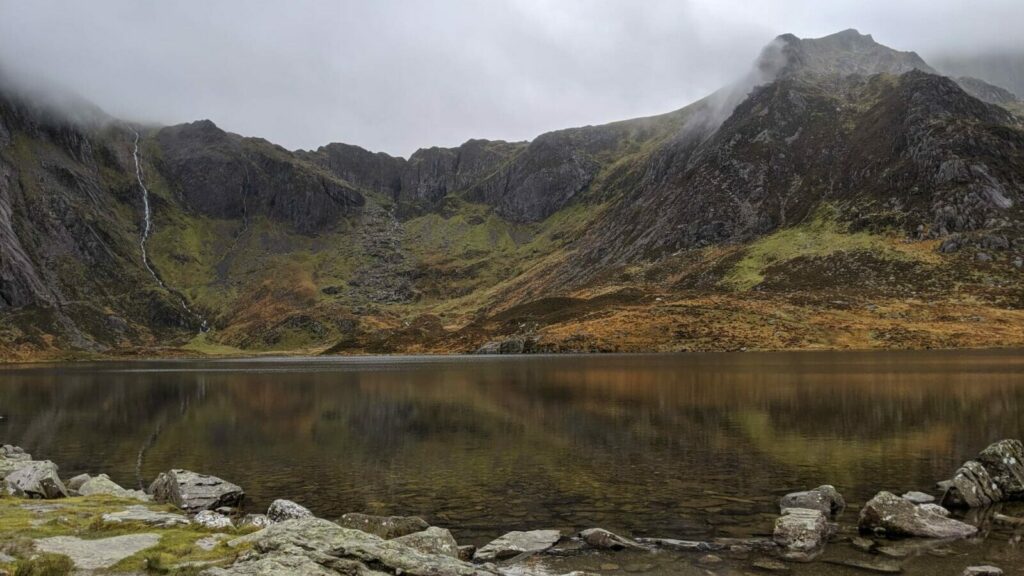

Tectonic collisions
The ancient Iapetus ocean is closed as the Laurentia and Avalonia tectonic plates move towards each other and collide. This caused the plates to buckle and fold under the pressure, forcing the earths surface upward, creating a huge mountain range. These folds are seen today in the Cwm Idwal syncline.
2.7 Million – 10,000 years ago
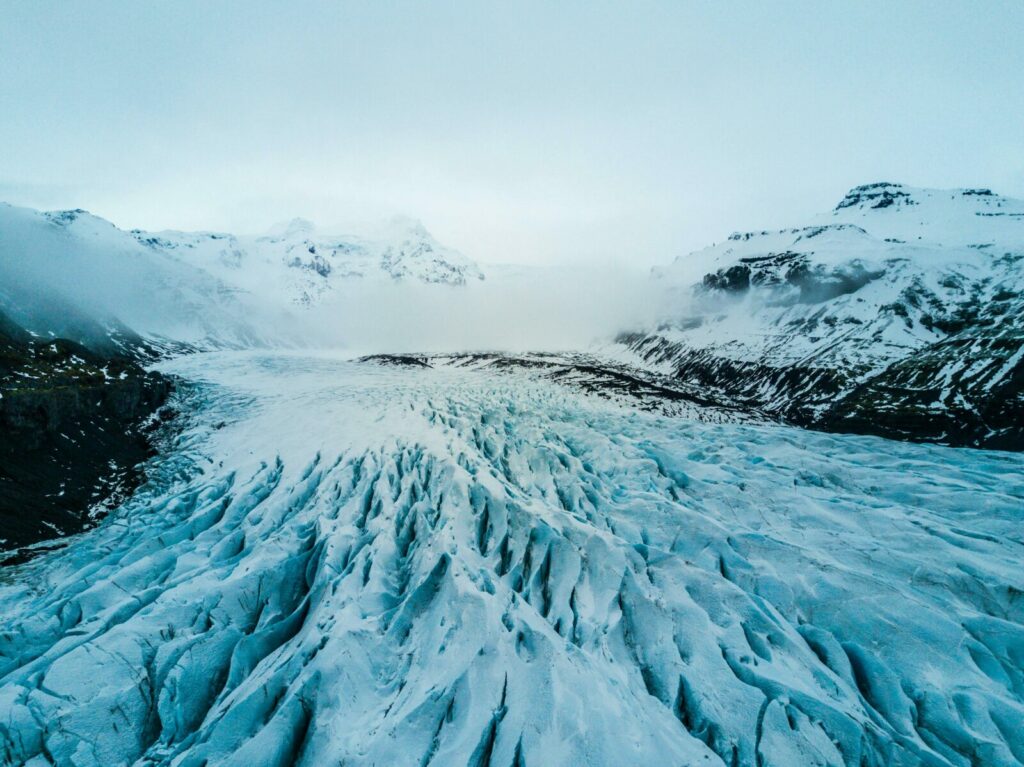

Ice Age
A sequence of cold periods cover Eryri in ice and glaciers. The last cold period “The Ice Age” comes to an ed around 10,000 years ago and is responsible for the landforms we recognise in Eryri today.
9,000 – 6,000 years ago
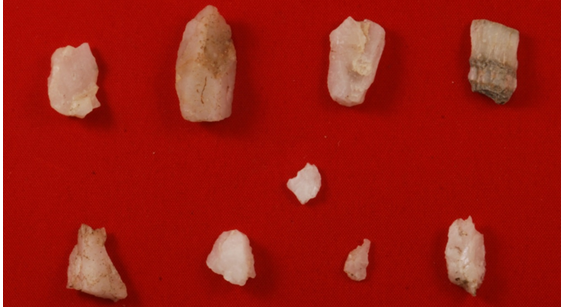
Mesolithic age
Evidence of people living in Cwm Idwal include tool parts made of quartz and remains of old hut circles.
2,500 BCE – 43 CE

Bronze Age & Iron Age
Change in agricultural and land use patterns. Development of a “Celtic” language and culture.
5th Century – 15th Century
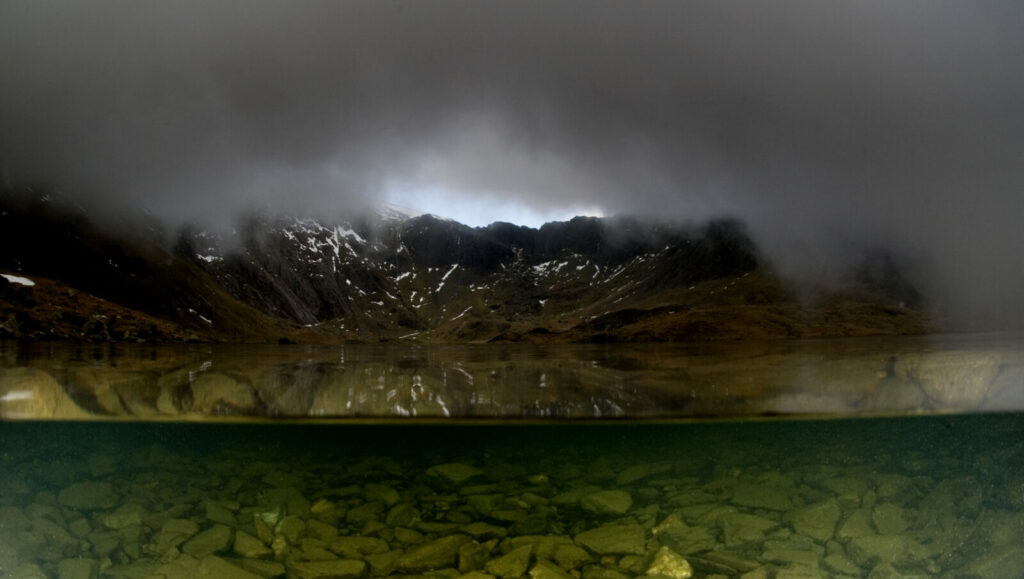

Medieval Age
Welsh Culture. The age of the Welsh Princes. Many place names and myth have their roots in these times such as Carnedd Llywelyn and Yr Elen, and the myth of Llyn Idwal.
1773
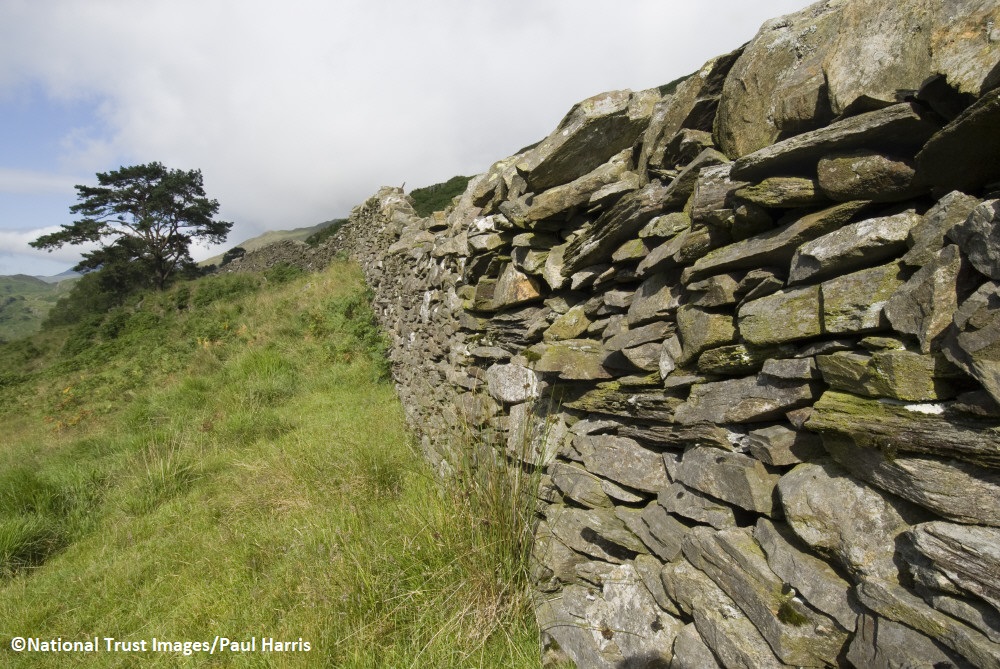

Land Enclosure Act
The rights of the common people are reduced and a significant change in agricultural patterns in Eryri. Land is “improved”, drains, walls and fences are built. People are forced to abandon the rural uplands for the towns and cities.
1895

The National Trust is formed.
The National Trust was formed to care for nature, beauty and history for everyone. The Trust acquired their first property in the same year, Dinas Oleu near Barmouth.
1939 – 1945
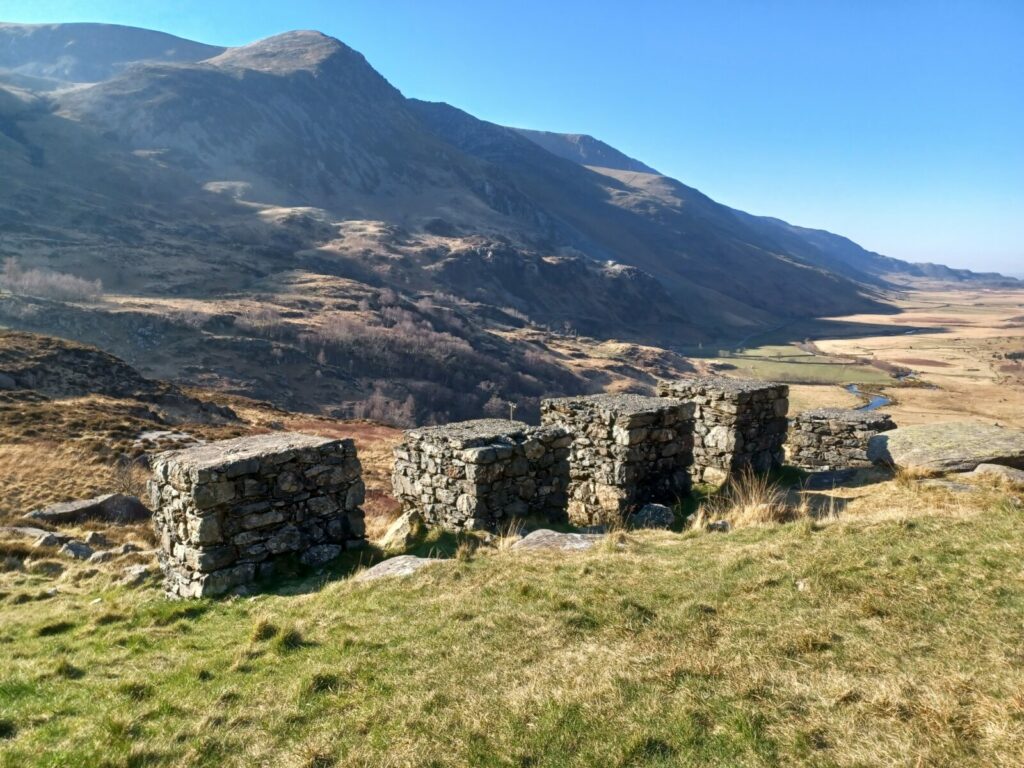

The Second World War
Large demand to increase agricultural production during and after the war. Remains of eth Home Guard can still be seen in the landscape, including pillboxes and tank traps.
1949

National Parks and Countryside Act
This establishes the Nature Conservancy body – a precursor to Natural Resources Wales. Opens the door to establishing National Parks in the UK.
1951

Eryri National Park is established
Eryri National Park is established – the third in the UK to protect natural beauty and promote learning and enjoyment of the area by the public.
The lands of the Penrhyn Estate are transferred over to the National Trust.
1954

National Nature Reserve
Cwm Idwal is designated Wales’ first National Nature Reserve because of the geological features at the site and the rare arctic-alpine plants living there.
1970s
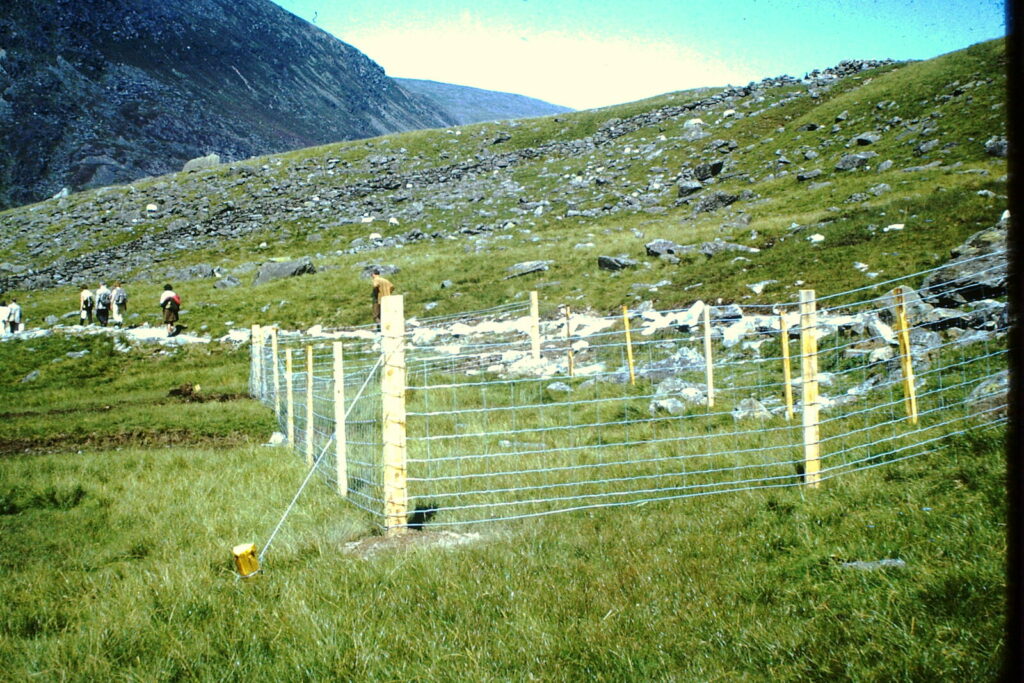

Grazing Plots
1970s

Grazing plots
Small plots are fenced off in Cwm Idwal to prevent grazing.
1998
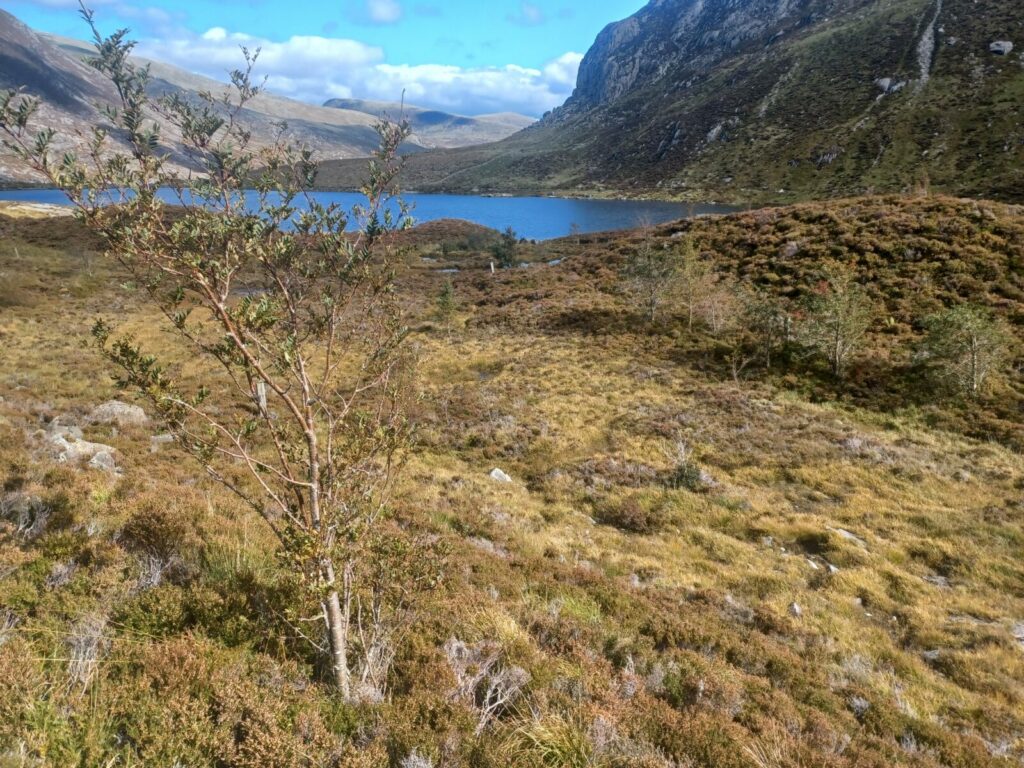

Grazing is abolished in Cwm idwal
Grazing sheep and cattle are abolished in Cwm Idwal as part of a log term experiment to observe the effect removing grazing pressure will have on the vegetation.
2000
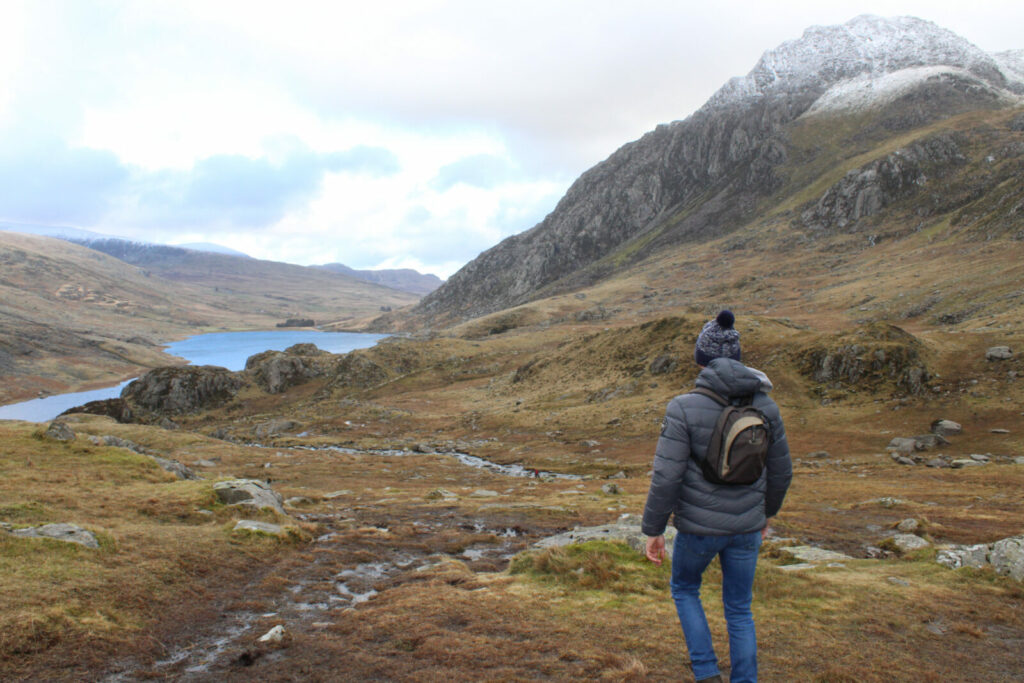

Countryside and Right of Way Act
The act strengthens and extends the public’s rights of access.
2010
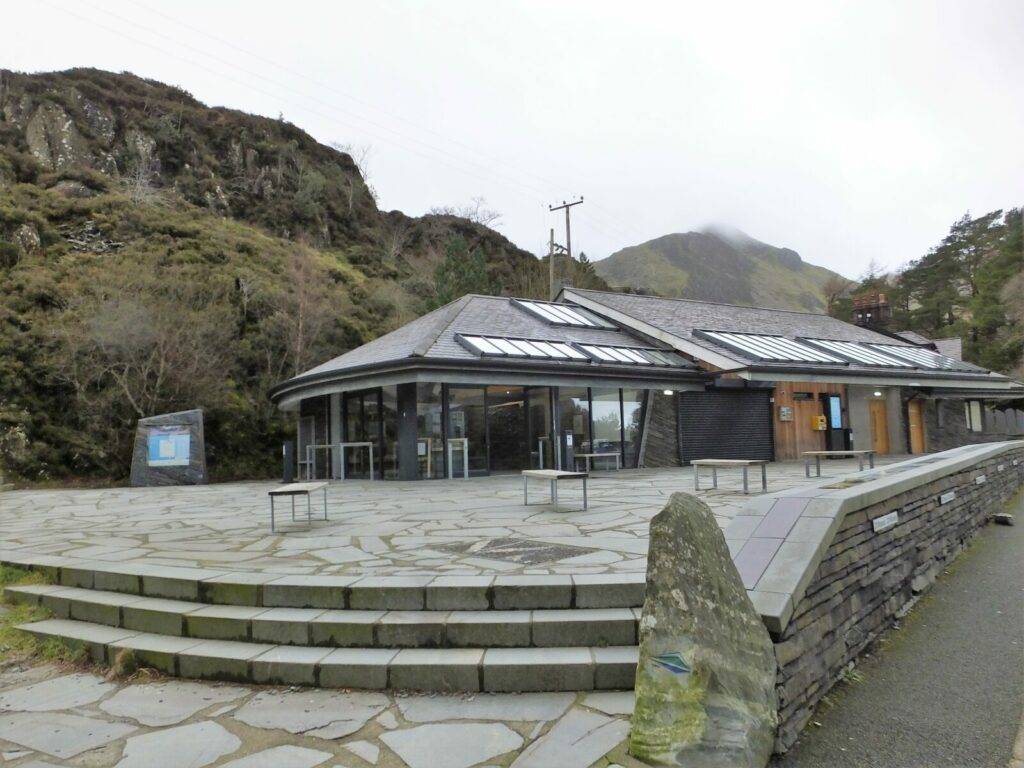

Cwm Idwal Partnership
Eryri national Park, the National Trust and Natural Resources Wales (Countryside Council for Wales) agree to for a partnership to better interpret, educate and care for Cwm Idwal
2013

Natural Resources Wales
The Countryside Council of Wales, the Environment Agency and the Forestry Commission join to create Natural Resources Wales. They ensure that Wales’ natural resources are sustainably maintained, enhanced and used, now and in the future.
2020

Brexit
The UK leaves the European Union.
2020-2021

Coronavirus Pandemic
Access to Cwm Idwal is closed during the Covid lockdowns. Significant change in the visits to Cwm Idwal following the end of lockdown. Cwm Idwal becomes more popular than ever partly due to the influence of social media.
2024 –
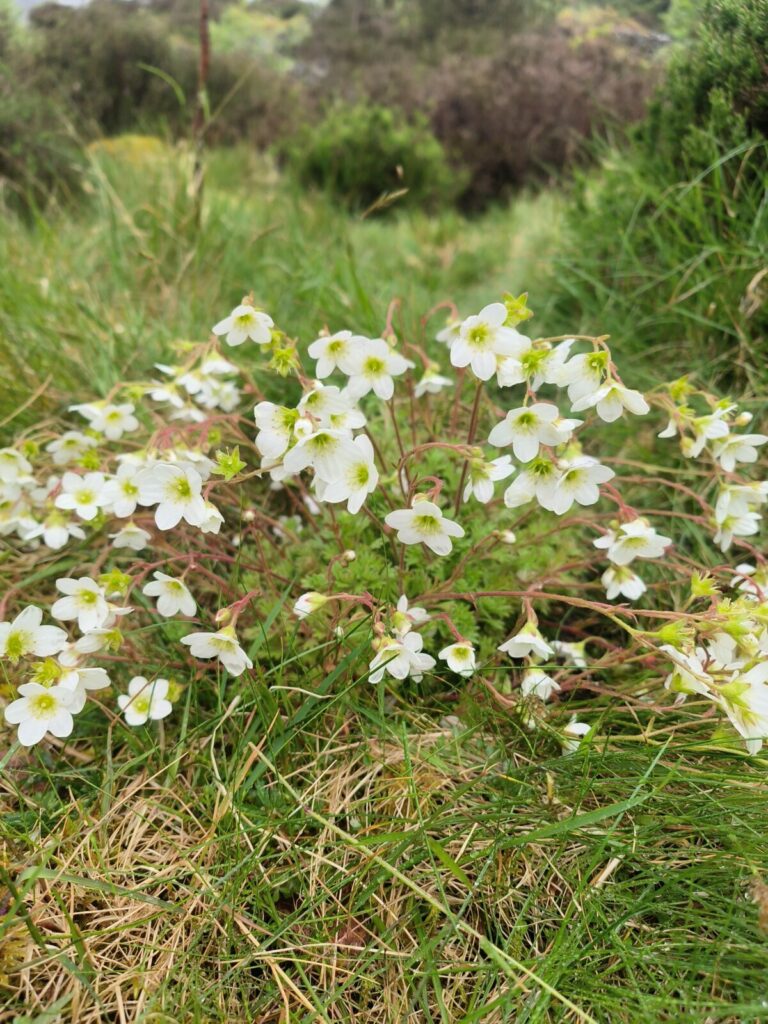

Natur Am Byth Project
Natural Resources Wales launch the Natur Am Byth (Nature Forever) project to help endangered species across Wales. In Eryri the charity Plantlife leads a sub-project called Tlysau Mynydd Eryri (Eryri Mountain Jewels) which aims to restore and strengthen the populations of rare arctic-alpine species in Cwm Idwal.